The LandLabs are a tool to support knowledge transfer and activate regional landscape resilience solutions in 5 selected Mediterranean regions.
Landlabs are context specific knowledge transfer and engagement programs for farmers and foresters in selected regions that represent important areas for climate change impacts.
To do so, the LandLabs will carry out different activities, such as events, workshops, field trips, and showrooms. In this sense, the development of the LandLabs will allow stakeholders to identify and adapt the best solutions for each region. Because the LandLabs have a specific regional focus and the activites will be in-presence and in local language, we suggest you join the LandLab that is closer to you.
Introducing Your Innovative Landscape Resilience Practice!
Explore the forefront of sustainable practices with ResAlliance! If you’re a trailblazer addressing climate change in the Mediterranean, share your innovative story through captivating videos (up to 3 minutes) or compelling written narratives (up to 4 pages).
Recognition Awaits!
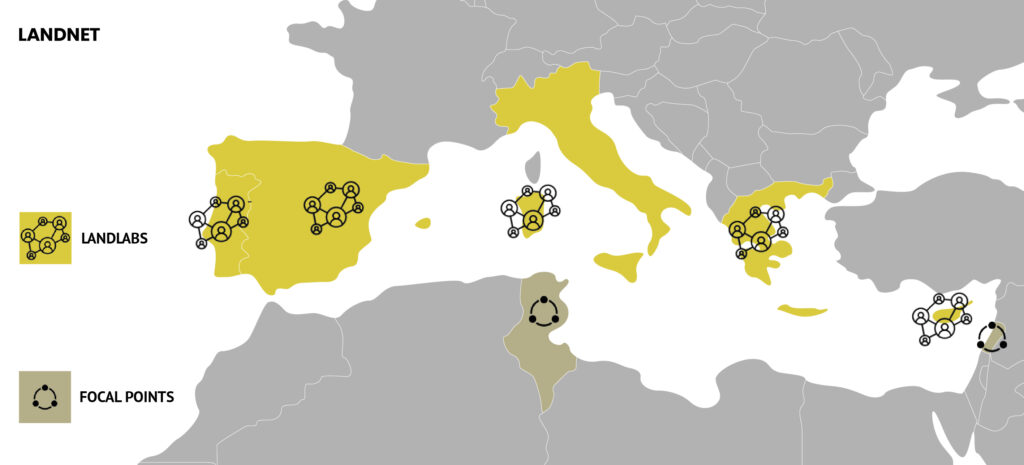
Where are the LandLabs?
The LandLabs will be developed in 5 Mediterranean regions that are highly exposed to climate change hazard occurrence: Sardinia (Italy), Catalonia (Spain), Peloponnese (Greece), Cyprus and Regiao Norte (Portugal).
While these regions share the threats posed by typical Mediterranean hazards aggravated by climate change – especially wildfires and droughts – each region has specific social needs and agricultural and forestry challenges that call for tailored solutions.
Location: Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro (Bragança and Vila Real) and Alto Minho sub-regions
Challenges: The region is greatly shaped by smallholding property and an agroforest mosaic landscape, characteristics that enhances resilience and adaptation to climate changes and other hazards, but simultaneously increase the challenges around management and governance. Together with a highly productive forest (wood and paper) and silvopastoral (meat with protected origin) sectors, different agroforest productions such as acorns, chestnuts, resin, mushrooms, honey, vineyards or cork are present. The establishment of economic ranks and increase added value around these productions are additional challenges.
Needs: Increase the society’s awareness of the rural landscape potential, reduce wildfire risk and other hazards, increase and demonstrate the profitable economic value from forest and agroforest areas, promote innovation around non-wood forest products, favour the adaptation of agriculture and forest species to climate change and promote adequate restoration management of ecosystems, such as the ones affected by climate change, wildfires and other hazards.
Location: Baix Llobregat and Alt Penedès counties
Challenges: Agricultural or dense forest landscapes entangled, in some cases, within high-density urban and industrial areas
Needs: Promote forest practices to reduce the vulnerability to wildfires and drought, foster agricultural practices to reduce the exposure to drought and high temperatures and restoration of mosaic patterns landscape for climate change adaptation
.
Location: Forest districts of Goceano/Gallura and Grighine/Montiferru
Challenges: High dependency on the extraction and production of cork, which is reduced by drought; forest fires and lack of awareness of the local population
Needs: Improving forecasting systems for planning cork extraction; identifying how these areas can be supported to ensure a profitable economic value from cork and olive growing; raising awareness against wildfire events, specifically within wildland-urban interfaces; engaging local people to promote best restoration and disaster management practices
Location: Peloponnese peninsula
Challenges: Enhance landscape resilience against wildfires, second highest in Greece
Needs: Awareness and knowledge on integrated land management approaches to strengthen the areas of agricultural production (wine and olives, honey); increasing local farmers and foresters’ awareness of wildfire risks and mitigation and adaptation measures, especially in realtion of production methods; supporting the development of policies to improve landscape resilience to climate change
Location: Troodos mountains and Akamas National Forest Park
Challenges: Dryness, high temperatures, abandonment of rural areas and lack of managed forests leading to high risks of large wildfires; legislative and administrative fragmentation which halt the application of integrated and innovative landscape management solutions
Needs: Promoting the development of the primary sector and rural areas and using ancestral forestry knowledge and holistic landscape management
Why join the LandLabs?
Joining the LandLab, you will:
- actively participate in the LandLabs: 5 laboratories that allow you to get to know other subjects in the agricultural and forestry sector, and exchange with them knowledge and good practices developed in the area to deal with the great challenges posed by climate change;
- have the opportunity to personally contribute to new strategies for managing these challenges;
- participate in Showrooms, where you will have the chance to know the ResAlliance project and get information on emerging results;
- 3 month MOOC in which effective and operational training on the issues of landscape resilience in the field of agriculture and forestry will be guaranteed;
- Receive the project Newsletter in which the information materials that will be created during the project are shared, thanks to the exchange of knowledge that will take place in the 5 project countries.
LandLabs are part of the LandNet; join a LandLab by filling in the LandNet registration form.